





Related Attributes
Product details
Application in food industry: B-D-galactosidase is mainly used in the dairy industry. It can convert low-sweetness and low-solubility lactose into sweeter, more soluble monosaccharides (glucose and galactose), thereby improving the sweetness and taste of dairy products.
In addition, it reduces the likelihood of lactose crystals precipitating in ice cream, concentrated milk, and light condensed milk, further improving the quality of the product. In the fermentation and baking industries, B-D-galactosidase facilitates the fermentation and baking process by making lactose, which cannot be utilized by normal yeast, available due to hydrolysis to glucose12 .
Applications in the medical field: B-D-galactosidase also has some applications in the medical field. For example, some infants suffer from diarrhea after milk feeding due to the lack of normal lactase-degrading enzymes in the intestine.
Therefore, lactase and lysozyme are often added to milk for infants in many European countries to help them digest lactose2 .

Uses of Beta Galactosidase.
Beta-galactosidase is mainly used in the dairy industry.
It converts low-sweetness and low-solubility lactose into sweeter, more soluble monosaccharides (glucose and galactose); it reduces the likelihood of lactose crystals precipitating out of ice cream, concentrated milk, and evaporated condensed milk, while increasing sweetness. In the fermentation and baking industry, it enables lactose, which cannot be utilized by yeast in general, to be utilized due to hydrolysis to glucose.
There are a certain number of infants due to the lack of normal lactose catabolic enzymes in the intestines and lead to diarrhea after feeding milk, so many European countries often add lactase and lysozyme to milk for infants to drink.
Pharmacological effect of Beta Galactosidase.
Product Method of Bulk Beta Galactosidase Powder.
The whey obtained from cheese-making was heated to coagulate at pH 4.5 and a temperature of 85 to 105°C. 0.1% ammonia was added to the coagulum, and yeast strains (e.g., Saccharomyces fragilis) were accessed to incubate in an aerated culture at 30°C. The yeast was collected, washed with lukewarm water, and then cooled sharply at -18°C to deactivate other enzymes contained therein, and was treated with ethanol in an amount of 1.5 to 3.0 times the amount of yeast. The yeast was then treated with 1.5 to 3.0 times the amount of yeast in ethanol.
WHY CHOOES US?

OUR CERTIFICATE

CUSTOM PROCESS

OUR PACKAGE

OUR EXHIBITION

OUR FACTORY

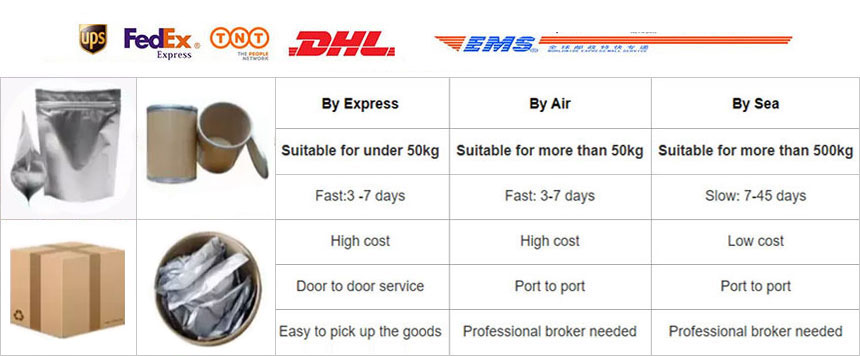
Shipping
Pharmaceutical Intermediate manufacturers
©2022 Xi'an Henrikang Biotech Co., Ltd.,