





Related Attributes
Product details
Azithromycin has a mechanism of action similar to that of erythromycin, exerting its antibacterial effect by binding to the 50S subunit of the ribosome of sensitive bacteria and inhibiting RNA-dependent protein synthesis, retaining the typical antibacterial spectrum of erythromycin. The activity against Chlamydia is similar to that of erythromycin.
Compared with erythromycin, the antibacterial activity against gram-negative bacteria has been significantly improved, the antibacterial activity against H. influenzae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae is more than 4 times stronger than that of erythromycin, the antibacterial activity against Legionella is about 2 times stronger, and the antibacterial activity against Enterobacteriaceae is also significantly stronger than that of erythromycin.
The MIC for most gram-negative bacteria is less than 1μg/ml.Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes are cross-resistant to this product and erythromycin. It also has good killing effect on Toxoplasma gondii and syphilis spirochetes.
Azithromycin is mainly used for respiratory tract infections, genitourinary tract infections, soft tissue skin infections and sexually transmitted diseases caused by sensitive microorganisms.

Uses of Azithromycin.
Antibiotics for infections caused by sensitive bacteria, such as respiratory infections, skin and soft tissue infections.
Used for respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections and sexually transmitted diseases
1. For acute pharyngitis, acute tonsillitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, sinusitis, acute otitis media,acute bronchitis, acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis caused by sensitive bacteria.
2. For pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, H. influenzae and Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
3. For urethritis, cervicitis and pelvic inflammatory disease caused by Chlamydia and non-multi-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and simple genital infections caused by non-multi-resistant gonococcus (co-infections with spirochetes of Treponema pallidum should be excluded).
4. For skin and soft tissue infections caused by sensitive bacteria.

Drug interactions of Azithromycin.
(1) Azithromycin should not be taken with antacids containing aluminium or magnesium, the latter can reduce the peak blood concentration of the product by 30%, but no effect on the total bioavailability has been seen; must be combined, the product should be given 1 hour before or 2 hours after taking the above drugs.
(2)When combined with theophylline, it can increase the concentration of the latter in the plasma; attention should be paid to the detection of plasma theophylline levels.
(3) When combined with warfarin, attention should be paid to checking the prothrombinogen time.
(4) Close observation of patients is recommended when azithromycin is used concomitantly with the following drugs:Digoxin: It has been reported that certain macrolide antibiotics may reduce the enteric metabolism of digoxin; therefore, when the two drugs are used together, attention should be paid to the possibility of elevated digoxin blood concentrations.
Ergotamine or dihydroergotamine: acute ergot toxicity with symptoms of severe peripheral vasospasm and dullness of sensation (pain on touch).
Triazolam: pharmacological effects of triazolam are enhanced by reducing its degradation.Cytochrome P450 system metabolising drugs a raise serum levels of carbamazepine, terfenadine,cyclosporine, cyclohexabarbital, phenytoin.
(5) The combination of azithromycin and rifabutin increases the toxicity of the latter.

Production Methods of Azithromycin.
Erythromycin A is used as raw material, which is oximilated and then subjected to Beckmann rearrangement under the action of hydrochloric acid, then dehydrated, reduced and methylated to obtain azithromycin.
WHY CHOOES US?

OUR CERTIFICATE

CUSTOM PROCESS

OUR PACKAGE

OUR EXHIBITION

OUR FACTORY

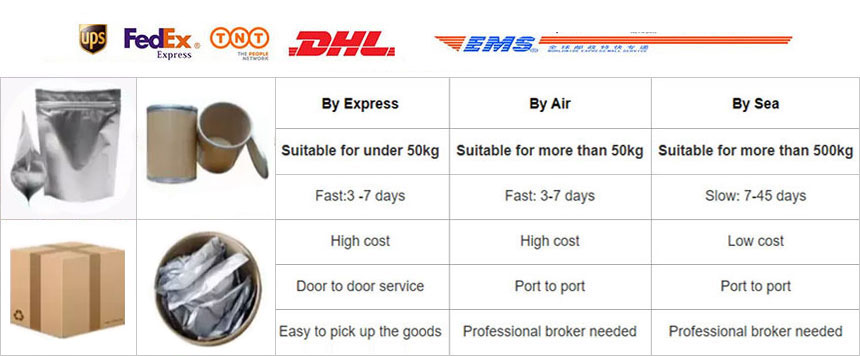
Shipping
Pharmaceutical Intermediate manufacturers
©2022 Xi'an Henrikang Biotech Co., Ltd.,