Pharmaceutical
Human APIs Powder
- Respiratory Drugs Raw Material
- Antiviral Antibacterial
- Antipyretic Analgesics
- Antihistamine Drugs
- Antineoplastic
- Cosmetic Raw Material
OEM & ODM
- Capsule
- Softgel Capsule
- Gummies
- Drop & drinks
- Tablets
- Effervescent Tablet
- Gel
- Powder
- Chewing Gum
- Pet Supplement
Veterinary raw materials
Phone: 86-13279202917
E-mail: sales@nutrition-oem.com
Add: Fengcheng 2nd Road, Weiyang District, Xi'an, Shaanxi, China
Bulk Soybean Polysaccharide Raw Powder supplier


Product Overview:
Soybean polysaccharides are high-purity, water-soluble polysaccharides obtained from soybeans or soybean processing byproducts using modern extraction techniques. They are primarily composed of galactose, arabinose, and rhamnose, and are a type of natural high-molecular-weight carbohydrate. Unlike common starches or colloids, soybean polysaccharides exhibit excellent stability and emulsifying properties even at low viscosity, and are extremely resistant to acid and heat, making them stand out in numerous industrial applications.
Product Attributes
Specification: 99% min Soybean Polysaccharide Powder
Sample: Soybean Polysaccharide Powder Avaliable
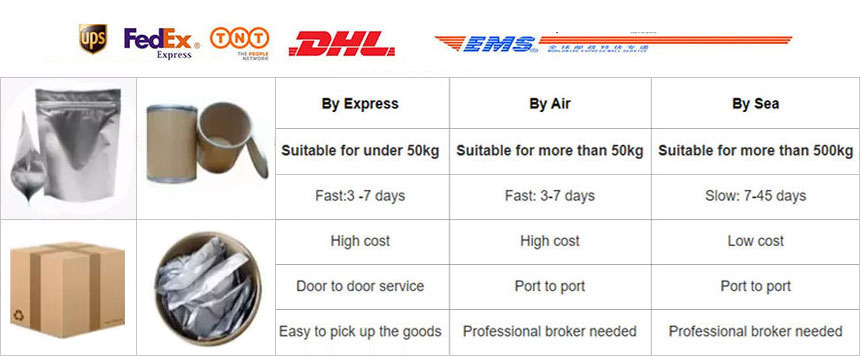
Packaging: 1kg/bag, 25kg/drum
Brand: Ausreson
MOQ: 1 kg
Appearance: White powder
Storage: Cool Dry Place
Shelf Life: 2 Years
Test Method: HPLC
Product Details
Soybean Polysaccharide Powder Usage and Synthesis.
Soya polysaccharide has a variety of biological activities and is a natural functional component that inhibits lipid oxidation and stabilises proteins in acidic beverages, which can improve the food quality, processing characteristics and appearance of food products. Water-soluble soybean polysaccharides have low viscosity and can be made into highly concentrated solutions, the viscosity of which is almost unaffected by salts, and their thermal stability to temperature is superior to that of other sugars.
In addition, dried soybean polysaccharide has strong adhesion and can form a film, so soybean polysaccharide can be used as a coating material.
Soybean polysaccharide has a variety of functions such as dispersion, stability, emulsification and adhesion, which can not only be used as dietary cellulose to fortify food, but also can be used in the pharmaceutical industry.
In addition, soybean polysaccharide has biological activities such as regulating blood glucose value and blood lipids, promoting the adsorption and excretion of harmful substances in the intestinal tract, and promoting the absorption and utilisation of minerals, and it also has a certain efficacy in antioxidant, anti-bacterial, anti-viral, and immune modulation.
Main Application Areas
- Food and Beverages: Widely used in acidic protein drinks, flavored yogurt, sauces, salad dressings, meat products, and baked goods as a stabilizer, thickener, and texture improver.
- Health Supplements: As a key ingredient in dietary fiber supplements, used in powders, capsules, or functional snacks.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care: Utilizing its film-forming and moisturizing properties, it is used in lotions, masks, and other products, providing natural and gentle formulation options.

Uses of Soybean Polysaccharide.
Soybean polysaccharide is mainly made from soybean protein processing or soybean residue fibre, a by-product of soybean product processing such as tofu and bean curd, etc. It is refined by pretreatment, enzyme digestion (cellulase, hemicellulase, protease, etc.), separation, decolouration, sterilisation, drying and other processes.
Soybean polysaccharide is white to light yellow powder, low viscosity of aqueous solution, good taste, no bad smell. In addition to being an excellent water-soluble dietary fibre, Soya polysaccharide is also a high-performance emulsion stabilizer, especially in the acidic environment with a unique stabilisation of protein emulsified fat properties.
Preparation of Soybean Polysaccharide.
(1) Soya bean oil residue with impurities such as husk, scorched particles and sand removed was crushed and collected as fine particles passing through a 40 mesh sieve.
(2) Take 200 g of oil dregs and 2000 g of hexane and add them to a fat extractor consisting of a reflux condenser, an extractor and a flask for 1 hour of extraction. The oil dregs obtained from the extraction were dried at 60-70°C for 1 hour to remove the residual solvent.
(3) 100 g of the extracted oil residue was mixed with 1000 ml of sodium hydroxide solution at a concentration of 13%, heated to 50°C in a water bath, and extracted for about 1 hour under constant stirring.
( (4) The extract was filtered under reduced pressure, the filtrate was retained, and the filter residue was further extracted with sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 10%, the amount of sodium hydroxide solution added was 10 times the weight of the filter residue, the extraction temperature was 50°C, and the extraction time was 30 to 45 minutes.
(5) The secondary extract was filtered under reduced pressure, and the filtrate obtained from the two extractions was combined and used to extract soy protein. A 10% concentration of sodium hypochlorite solution at 3 times the weight of the filtrate was added to the filtrate, and the pH of the mixture was adjusted to 10 to 11. The filtrate was decoloured by stirring for 40 minutes at room temperature.
(6) The decolourised solution was filtered under reduced pressure, the filtrate was discarded, the filter residue was washed with pure water at 40~50°C until the wash solution was neutral, and then filtered under reduced pressure, and the resulting filter residue was washed once with ethanol and once with acetone, and then drained.
(7) The drained filter residue was dried in a vacuum oven at 80 ℃ for 1 hour, until the moisture content was less than 8%, cooled to room temperature for crushing. Crushed material through a 100-mesh sieve, the production of light yellow, slightly flavoured powdered soybean polysaccharide.

Functional characteristics of Bulk Soybean Polysaccharide Powder.
1.Physiological health care function of soybean polysaccharide not only has the general dietary fibre functions, such as: promote intestinal peristalsis, weight loss, lower blood pressure, lower serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels, lowering blood glucose, enhance high-density lipoprotein, reduce low-density lipoprotein, and the prevention of certain cancers, etc., but also regulate the balance of microbial nutrition in the gastrointestinal and cholesterol metabolism, and inhibit the oxidation of lipids in immune serum. 2. It can also regulate the balance of microbial nutrition in gastrointestinal and cholesterol metabolism and inhibit the oxidation of lipid in immune serum.
2. Stabilisation of protein under acidic conditions Acidic protein beverages are often subject to protein precipitation, and stabilisers such as pectin are often added to stabilise acidic protein beverages. Carboxymethylcellulose, carrageenan and propyleneglycol alginate are also commonly used stabilisers in acidic milk beverages, and in general pectin and carboxymethylcellulose are used to stabilise acidic milk beverages by increasing the viscosity of the beverages. In general, pectin and carboxymethyl cellulose mainly stabilise protein drinks by increasing their viscosity, which is lower than that in drinks containing soya bean polysaccharides, so that acidic milk beverages can be obtained without viscosity and are more refreshing, and are not affected by the concentration of salt ions in the system and the pH.
FAQ
Q1: Is soy polysaccharide suitable for people with allergies?
A: Soy polysaccharide is a carbohydrate extracted from soybeans with extremely low protein content, and generally does not cause allergic reactions to soy protein. However, for those with severe soy allergies, it is recommended to choose carefully under the guidance of a doctor. Please check the product specifications and allergen declaration when purchasing.
Q2: What are the advantages of soy polysaccharide compared to common colloids (such as gum arabic and pectin)?
A: Compared to many traditional colloids, soy polysaccharide exhibits superior stability under acidic, high-salt, and high-temperature conditions, and can maintain stability at low viscosity without affecting the original taste of the product. It also provides dietary fiber benefits, aligning with the trend towards clean labeling.
Q3: What is the recommended addition amount of soy polysaccharide in the final product?
A: The addition amount varies depending on the application, typically between 0.1% and 2.0%. For example, in acidic protein beverages, 0.5%-1.5% is sufficient to effectively stabilize the protein. The specific dosage needs to be determined experimentally based on the formulation, process, and desired effect.
Q4: Will soybean polysaccharides affect the flavor or color of food?
A: High-quality soybean polysaccharides are white to pale yellow powders. Their aqueous solutions are virtually colorless and odorless, having minimal impact on the original flavor and color of the product. They are ideal for beverages and foods with stringent flavor requirements.
Q5: Is it suitable for organic products?
A: Yes. Organically certified soybean polysaccharides are available on the market. Please be sure to request the relevant organic certificate from the supplier to ensure compliance with organic product regulations.
Поставщик сырого порошка полисахарида сои оптом
Fournisseur de poudre brute de polysaccharide de soja en vrac
Großhändler von Rohpulver aus Sojapolysaccharid
Proveedor de polvo crudo de polisacárido de soja a granel
Fornecedor de pó bruto de polissacarídeo de soja a granel
Inquire This Product