





Related Attributes
Product details
Chloramphenicol, also known as chloramphenicol, is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent produced by Streptomyces chlorostreptococcus with the effect of inhibiting bacterial growth, and the natural chloramphenicol is the levamycin (also known as levomycin).
The synthetic product is white or slightly yellow needle-like or flaky crystals, odourless, extremely bitter taste, slightly soluble in water, ether and chloroform, soluble in methanol, alcohol, acetone or ethyl acetate, insoluble in benzene and petroleum ether.
It is stable in neutral or weakly acidic aqueous solution, and easily invalidated by alkali. The synthetic product is the racemate, also known as haptomycin. Hemocycline is a mixture of chloramphenicol levodecamer and dextroamer. Because the dextrose has no antibacterial effect, the efficacy of synthomycin is only half that of the natural product.

Uses and functions of Chloramphenicol.
It is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, the first choice for the treatment of typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever, one of the special drugs for the treatment of anaerobic infections, followed by the treatment of various infectious diseases caused by sensitive microorganisms. Due to the serious adverse reactions now used less and less.
It is used for the treatment of infections caused by typhoid bacillus, dysentery bacillus, Escherichia coli, influenza bacillus, Borrelia burgdorferi, pneumococcus and so on.
What is chloramphenicol powder used for?
In humans, chloramphenicol is only used to treat severe, life-threatening infections where no other safer antibiotics are effective. These situations are rare and typically occur in a hospital setting.
Bacterial Meningitis: Used for certain types of bacterial meningitis when the causative organism is resistant to other drugs.
Typhoid Fever: Used for infections caused by Salmonella typhi that are resistant to other treatments.
Rickettsial Infections: For serious infections like Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever.
Topical Use: It is found in some eye drops and ointments for treating bacterial conjunctivitis (pink eye). This is a much safer route of administration as very little is absorbed into the body.
This is the most common context for chloramphenicol powder. A veterinarian may prescribe it for pets (dogs, cats, etc.) to treat various bacterial infections.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
Respiratory Infections
Gastrointestinal Infections
Certain Protozoal Infections: Like kennel cough caused by Bordetella.
Ear and Eye Infections: Often used in topical formulations.

Drug interactions of Chloramphenicol.
Chloramphenicol inhibits hepatic microsomal enzymes in the metabolism of phenytoin, toluene sulfobutylurea (methylsulfonylurea), chlorosulfopropylurea, and dicoumarin (and possibly other drugs), resulting in a prolonged half-life in vivo and an increase in serum concentrations.
Exacerbation of poisoning to the point of death has been reported. On the other hand, phenobarbital, phenytoin and rifampicin (Prober, 1985) reduce serum chloramphenicol concentrations, presumably due to the induction of hepatic enzymes by the drugs.
Therefore, serum chloramphenicol concentrations should be monitored if concomitant drugs that may affect the pharmacokinetic profile of chloramphenicol are used. Chloramphenicol delays the response of iron, folic acid and vitamin B12 to anaemia treatment. It also interferes with the host recall response to tetanus toxoid.
Therefore, the concomitant application of chloramphenicol with active immunisers should probably also be avoided. The clinical significance of chloramphenicol's antagonistic effect on the bactericidal action of penicillin remains unclear, although it has been demonstrated in vitro and in animal experiments.
Such combinations should be used only when the benefits of such treatment have been demonstrated.
Production Method of Bulk Chloramphenicol Powder.
The production methods of chloramphenicol have been studied a lot in the world and are summarised as follows:
(1) The p-nitroacetophenone method;
(2) Styrene method;
(3) Cinnamyl alcohol method;
(4) p-Nitrocinnamyl alcohol method;
(5) p-Nitrobenzaldehyde method.
China uses p-nitroacetophenone method, which is obtained from ethylbenzene by nitration, oxidation, bromination, salting, hydrolysis, acetylation, addition, reduction, decomposition, splitting, dichloroacetylation and chloramphenicol
WHY CHOOES US?

OUR CERTIFICATE

CUSTOM PROCESS

OUR PACKAGE

OUR EXHIBITION

OUR FACTORY

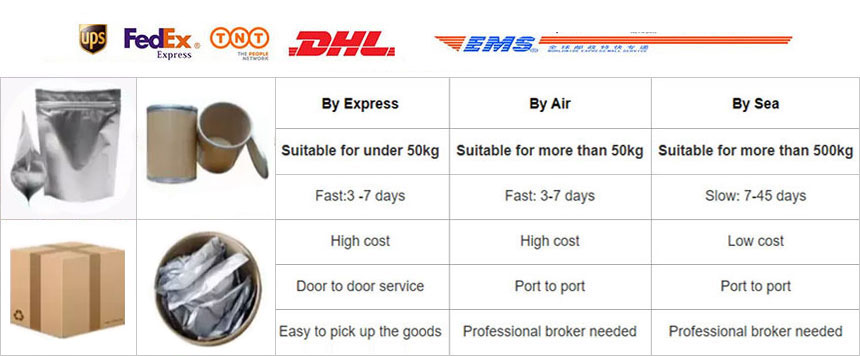
Shipping
Pharmaceutical Intermediate manufacturers
©2022 Xi'an Henrikang Biotech Co., Ltd.,