





Related Attributes
Product details
Glucoamylase is a type of amylase enzyme that is used in alcohols and wines, amylases, and the saccharification of starchy raw materials in a number of other fermentation industries.
Saccharifying enzyme, also known as glucoamylase, is a common name; its scientific name is α-1,4-glucan glucohydrolase. It is widely used in the industries of alcohol, starch sugar, monosodium glutamate, antibiotics, citric acid, and beer, as well as in the production of baijiu (Chinese white liquor) and huangjiu (yellow wine). Saccharifying enzyme is extracted from a superior strain of Aspergillus niger through deep fermentation.
Uses of Glucoamylase.
Glycoconjugate enzyme can catalyse the hydrolysis of starch to produce beer, yellow wine, sauce, monosodium glutamate and antibiotics; it is also used in the production of glucose, caramel and dextrin. It can be used in the production of fermented wine, distilled wine, alcohol and starch syrup according to the production needs.
Used for glycogen determination in yeast cells; relies on glycolytic enzymes to synthesise iso-oligosaccharides.
Usage Instructions
Advantages of use:
1. Saccharifying enzyme is non-corrosive to equipment and safe to use. The process using saccharifying enzyme is simple, its performance is stable, and it is beneficial for stable production in various plants.
2. Using saccharifying enzyme for starch hydrolysis is relatively safe, can increase the alcohol yield, reduce contamination by miscellaneous bacteria in the bran koji method, save grain, reduce labor intensity, and improve working conditions.
3. Using saccharifying enzyme promotes mechanization of production and facilitates civilized production.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the difference between glucosylamylase and α-amylase?
Both are starch-degrading enzymes, but their mechanisms of action are quite different. α-Amylase (EC 3.2.1.1) is an endonuclease that randomly cleaves long-chain starch into smaller dextrins and oligosaccharides. Glucoamylase (EC 3.2.1.3) is an exonuclease that cleaves individual glucose molecules one by one, starting from the ends of these chains. In industrial production, they are usually used sequentially: α-amylase for "liquefaction," and glucosylase for "saccharification."
Q2: Are there different types of glucosylamylase? How do I choose?
Yes, the main difference lies in the microorganism from which it originates. Fungal glucosylase from *Aspergillus niger* is the most common, favored for its acidic pH and good thermal stability. Glucoamylase from *Rhizopus* may have different adsorption characteristics for raw starch. The choice of enzyme depends on your substrate, process pH/temperature, and desired sugar profile. Consulting your enzyme supplier is always recommended for tailored advice.
Q3: What are the latest regulatory requirements for selling glucosylamylase in Europe?
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) significantly tightened its administrative guidelines by the end of 2025. The most pressing issues now are: ensuring your technical documentation is complete and accurate upon submission to avoid being publicly deemed "inadmissible"; notifying EFSA in advance before the start of the study; and ensuring all toxicology studies are conducted in laboratories compliant with OECD Good Laboratory Practices (GLP). Proactive planning and high-quality study design are more important than ever.
Q4: How is glucosylamylase used in bioethanol production? What are the application trends?
In traditional bioethanol production, glucosylamylase is added after the cooked, liquefied starch has cooled to convert all dextrins into fermentable glucose. Currently, a major trend in the industry is the shift towards "raw starch hydrolysis" or "integrated bioprocessing" (CBP). This method involves genetically engineering fermenting yeast strains to enable them to express and secrete their own glucosyl amylase, allowing saccharification and fermentation steps to be carried out simultaneously at lower temperatures, thus significantly saving energy and costs.
Product Methods of Glucoamylase.
This enzyme is mainly from Rhizoctonia solani and Aspergillus niger. In the production, it mainly adopts Aspergillus niger's mutant strain AS.3.4309 (referred to as UV I11) as the production bacteria, and takes corn flour (10%-12%), soybean cake powder 4%, corn syrup 2%, bran 1%, etc. as the medium, and cultivates it in deep layer for 100h; the fermentation liquid is refined and dried to produce the powder.
Proveedor al por mayor de polvo de enzima glucoamilasa para suplementos
Fornecedor atacadista de pó de enzima glucoamilase para suplementos
Großhändler für Glucoamylase-Enzympulver als Nahrungsergänzungsmittel
Fournisseur en gros de poudre d'enzyme glucoamylase pour compléments alimentaires
Оптовый поставщик порошка фермента глюкоамилазы для пищевых добавок
WHY CHOOES US?

OUR CERTIFICATE

CUSTOM PROCESS

OUR PACKAGE

OUR EXHIBITION

OUR FACTORY

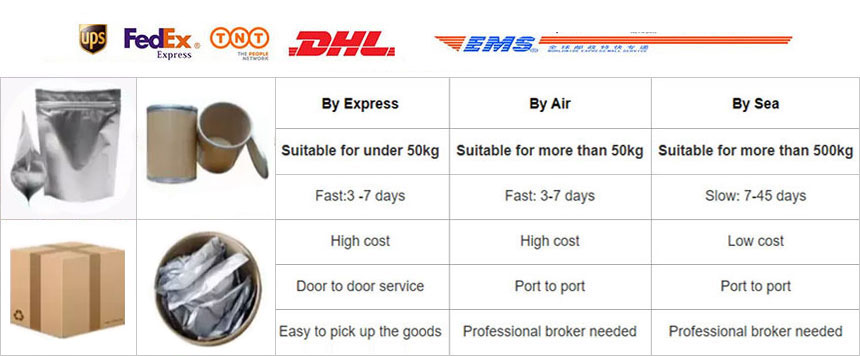
Shipping
Pharmaceutical Intermediate manufacturers
©2022 Xi'an Henrikang Biotech Co., Ltd.,