







Related Attributes
Product details
Monohydrate vs. Heptahydrate
When sourcing Zinc Sulphate Powder, the first technical decision involves the level of hydration.
Zinc Sulphate Monohydrate ($ZnSO_{4} \cdot H_{2}O$): Contains approximately 35% elemental zinc. This is the preferred form for dietary supplements and animal feed due to its high zinc concentration and superior shelf stability.
Zinc Sulphate Heptahydrate ($ZnSO_{4} \cdot 7H_{2}O$): Contains roughly 22% elemental zinc. Its high solubility makes it the "Gold Standard" for liquid fertilizers and water treatment applications across Europe and the US.
Industrials
Zinc sulfate is the main raw material for the manufacture of zinc barium white and zinc salts, and is also used as a mordant for printing and dyeing, a preservative for wood and leather, and an important auxiliary raw material for the production of viscose and vinylon fibers. In addition, it is also used in the electroplating and electrolysis industries, and can also be used to manufacture cables.
Cooling water in industry is the largest amount of water. Cooling water in the closed loop cooling system can not have corrosion and scaling on the metal, so it should be treated, this process is called water quality stabilization, zinc sulfate is used here as a water quality stabilizer.
Medicine
Oral zinc sulfate can correct zinc deficiency and restore the function of enzyme system. Zinc ions can precipitate proteins, topical use has astringent antiseptic effect, and can help the formation of granulation tissue. Pharmaceutical zinc sulfate is suitable for the treatment of enteropathic acral dermatitis, aphthous ulcers, chronic ulcers, conjunctivitis, etc. caused by zinc deficiency. However, sharing with penicillamine can weaken the latter's effect. Zinc sulfate monohydrate can be used as a zinc supplement in feed.

Pharmacological effect of Zinc Sulphate.
Zinc is a component of many enzyme systems (e.g., carbonic anhydrase, ethanol dehydrogenase, and alkaline phosphatase), and zinc deficiency can lead to abnormal enzyme function.
Oral zinc sulfate can correct zinc deficiency and restore the function of enzyme systems. Zinc ions can precipitate proteins, have astringent and antiseptic effects when used externally, and can help the formation of granulation tissue.
It is suitable for the treatment of enteropathic acral dermatitis, aphthous ulcers, chronic ulcers and conjunctivitis caused by zinc deficiency. However, the latter effect can be weakened by sharing with penicillamine. Plasma, liver, glandular pancreas and skeletal tissues are places of rapid zinc exchange and storage and are sensitive to changes in daily zinc levels.
Zinc affects animal growth, development and reproductive function, bone and blood formation and nucleic acid, protein and carbohydrate metabolism. It is associated with hair growth, skin health, and wound healing. On these tissues, zinc binds primarily to enzymes, acting as an essential constituent and activator of enzymes.
Zinc is a molecular component of carbonic anhydrase carboxypeptidase of the pancreas, glutamate and lactate dehydrogenase. It activates uricase, dipeptidyl peptidase in intestinal fluids and other enzymes. It can act indirectly on the reproductive function through its action on the pituitary gland and gonadotropins. Zinc sulfate monohydrate can be used as a zinc supplement in feed.

Key Applications and Benefits of Zinc Sulphate Powder
1. Human Nutrition & Dietary Supplements:
Immune System Support: Zinc is vital for the normal function of immune cells. Supplementation with Zinc Sulphate can help reduce the duration and severity of common colds and support overall immune defense.
Cellular Growth & Repair: Zinc plays a critical role in cell division, protein synthesis, and wound healing, making it essential for growth and recovery.
Skin Health: Its role in cell regeneration and anti-inflammatory properties make it a common ingredient in supplements aimed at combating acne and promoting clear skin.
2. Agriculture & Horticulture:
Essential Micronutrient Fertilizer: Zinc is a crucial micronutrient for plants. Zinc Sulphate is widely used in agriculture to correct zinc deficiencies in soil, which can stunt growth and reduce crop yields.
High Bioavailability for Plants: Its water-soluble nature makes the zinc readily available to plants, leading to quick greening and improved plant health.
3. Industrial & Miscellaneous Uses:
Animal Feed Supplement: Added to livestock and poultry feed to ensure proper growth, immune function, and reproduction.
Water Coagulation: Used in the production of rayon and as a coagulant in the production of glue.
Laboratory Reagent: A common chemical in analytical chemistry and other laboratory processes.
Zinc Sulfate vs. Other Forms of Zinc
Zinc Sulfate: This form contains a relatively high percentage of elemental zinc (about 23%). It is very effective and cost-efficient for treating a diagnosed deficiency. However, it is less well-absorbed and can be more likely to cause stomach upset than some other forms.
Other Common Forms:
Zinc Picolinate/Glycinate/Bisglycinate: These are chelated forms, meaning the zinc is bound to an amino acid. They are generally better absorbed and gentler on the stomach. Often preferred for daily supplementation.
Zinc Gluconate: Commonly used in cold lozenges and over-the-counter supplements. Well-tolerated.
Zinc Citrate: Also well-absorbed and a common choice in multivitamins.
What is the primary role of zinc sulfate powder in agriculture?
Zinc sulfate primarily functions as a zinc micronutrient fertilizer in agriculture, used to correct zinc-deficient soil conditions. Approximately 50% of U.S. farmland suffers from zinc deficiency. Applying zinc sulfate enhances crop yields, boosts disease resistance, and improves nutrient absorption efficiency.
What distinguishes feed-grade from industrial-grade zinc sulfate?
Feed-grade zinc sulfate prioritizes animal safety and bioavailability, with stringent limits on heavy metal impurities. Industrial-grade formulations are optimized for specific applications—such as textile dye mordants or wood preservatives—and may have specialized requirements for particle size and solubility.
How should zinc sulfate powder be stored correctly?
Zinc sulfate should be kept in its original, unopened container within a clean, dry warehouse. Due to its hygroscopic nature, exposure to moisture must be avoided. Long-term storage may require specialized temperature-controlled facilities, particularly in regions with variable climates like the U.S. Midwest.
What is the price trend for zinc sulfate?
Zinc sulfate pricing is significantly influenced by fluctuations in the zinc metal market, as raw material costs account for 60-65% of production expenses. Since 2022, zinc spot prices have fluctuated between $2,400 and $3,800 per metric ton, prompting producers to implement raw material surcharges. However, major buyers are increasingly resisting this practice.
Производитель высокочистого сульфата цинка (порошок, чистота не менее 99%, оптом)
Fabricant de sulfate de zinc de haute pureté (poudre, pureté min. 99%, en vrac)
Hersteller von hochreinem Zinksulfat-Pulver (Mindestreinheit 99%, Großhandel / lose Ware)
Fabricante de sulfato de zinc de alta pureza (polvo, pureza mínima del 99%, a granel)
Fabricante de sulfato de zinco de alta pureza (pó, pureza mínima de 99%, a granel)
WHY CHOOES US?

OUR CERTIFICATE

CUSTOM PROCESS

OUR PACKAGE

OUR EXHIBITION

OUR FACTORY

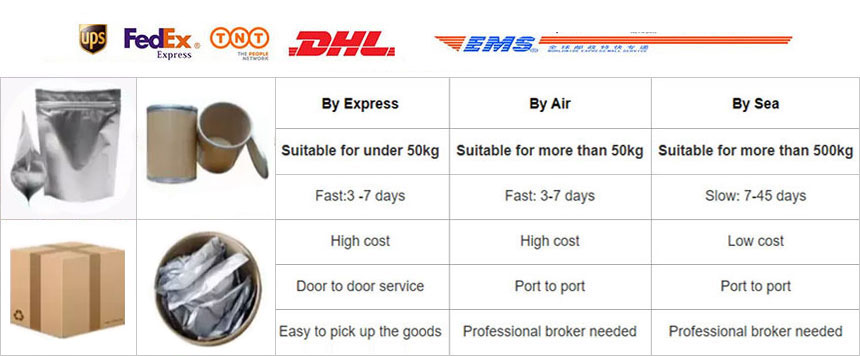
Shipping
Pharmaceutical Intermediate manufacturers
©2022 Xi'an Henrikang Biotech Co., Ltd.,